Facebook pissed off journalists earlier this year when it announced that ads run by news publishers to promote their articles involving elected officials, candidates, and national issues would have to sport “paid for by…” labels and be included alongside political campaign ads in its ads transparency archive that launched in June, albeit in a separate section. The News Media Alliance representing 2000 newspapers including the New York Times and NewsCorp plus other new organizations sent a letter to Mark Zuckerberg in June protesting their inclusion. They claimed it would blur the lines between propaganda and journalism, and asked Facebook to exempt news publishers.
Now Facebook has granted that exception. Legitimate news organizations who publish with bylines and dates, cite sources, and don’t have a history of having stories flagged as false by third-party fact checkers will no longer have their ads appear in the Ads Archive. They also won’t have to carry a “Paid for by…” label when they appear in the News Feed or Instagram. The change will also allow news outlets to run “dark post” ads that target specific users but don’t appear on their Pages. This will allow them to secretly test different ad variants without being exposed to potential criticism or competitors looking to copy their ad strategies.
Facebook will be using its recently built news publisher index that outlets can apply to to decide which ad buyers are exempt. That index is up and running in the US and will expand to other countries, but for now Facebook is using a third-party list of legitimate UK news outlets who’ll be exempted.
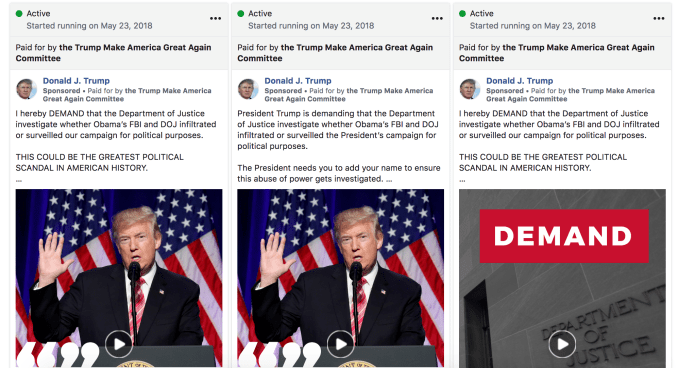
Facebook’s political ads archive of campaign ads will no longer include publications promoting articles about politics or issues
The change comes as Facebook rolls out enforcement of its political ads transparency rules in the UK today. “Now political advertisers must confirm their identity and location, as well as say who paid for the ad, before they can be approved to run political ads on Facebook and/or Instagram” Facebook tells TechCrunch. These ads will also feature the “Paid for by…” label. Facebook hoped that by self-regulating ads transparency, it might avoid more heavy-handed government regulation, such as through the US’s proposed Honest Ads Act that would bring internet political advertising to parity with transparency rules for television commercials.
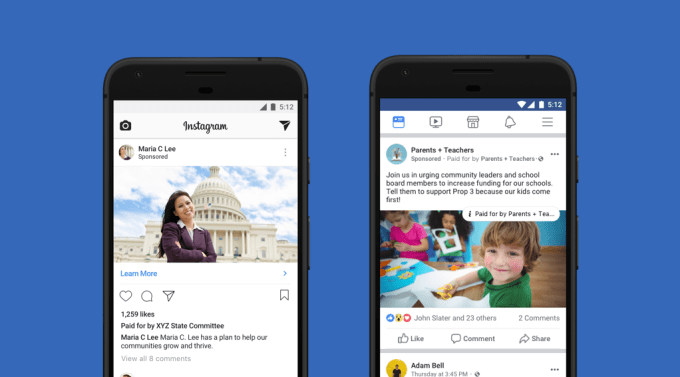
Facebook’s “Paid For By…” labels will no longer appear on news publishers’ ads on Facebook or Instagram
The hope is that by determining who is paying for these ads, properly labeling them, and exempting journalists, Facebook will be able to better track foreign misinformation campaigns and election interference. Meanwhile, users will have a better understanding of who’s funding the political and issue ads they see on Facebook.